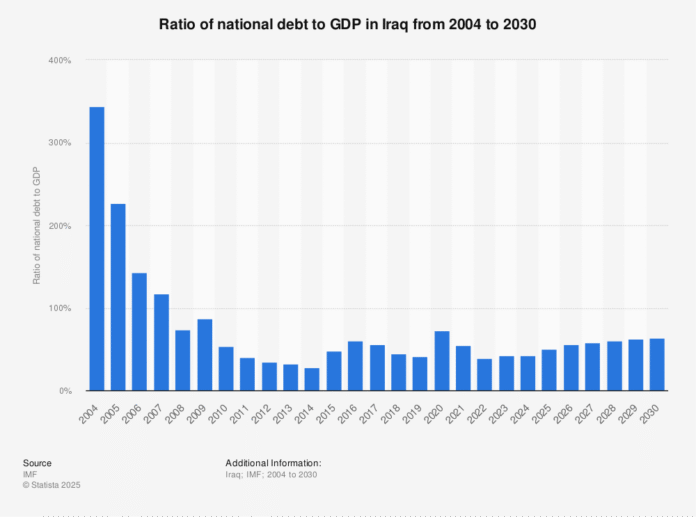
Iraq public debt remains stable at 43% of the nation’s GDP, according to the Central Bank of Iraq (CBI). The bank announced the figure on Sunday, October 19, 2025, highlighting that the ratio is moderate and within safe international standards. Iraq public debt continues to reflect careful fiscal management and strategic planning by the government and CBI.
The announcement clarified confusion surrounding figures in the 2023-2025 triennial budget law. While the law projected a 91.5 trillion Dinar deficit, actual spending resulted in a smaller 35 trillion Dinar deficit. The government covered this amount using internal bonds and transfers, showing strong coordination with the CBI. These measures prevented Iraq public debt from rising to the initially forecasted high levels.
The CBI also shared a detailed breakdown of the country’s debt portfolio. External debt due for repayment totals less than $13 billion. This figure excludes older, unclaimed debts from previous regimes. The bank emphasized Iraq’s strong regional and international financial reputation, noting the country has never defaulted on obligations.
Internal debt reached 91 trillion Dinars. This total includes 56 trillion Dinars accumulated by the end of 2022, plus 35 trillion Dinars from the 2023-2025 budget deficits. Most of the internal debt is held within the state banking system, ensuring controlled financial risk.
Furthermore, the CBI revealed that specialized committees and international consulting firms are working to transform part of the internal debt into investment instruments. These efforts aim to create a National Fund for Internal Debt Management, converting liabilities into productive financial opportunities. This approach aligns with broader plans to diversify the Iraqi economy and enhance non-oil revenues.
The bank emphasized that Iraq public debt management forms part of a comprehensive vision for financial sustainability. Authorities continue to strengthen economic reforms, reduce risk exposure, and maximize investment potential. The government and CBI remain committed to maintaining fiscal discipline while supporting long-term growth.
In conclusion, Iraq public debt is carefully controlled, showing the country’s strong fiscal health. With strategic reforms, Iraq continues to safeguard economic stability and secure future financial growth.